how to interpret mean and standard deviation in research
If mean score for male students in a Mathematics test is less than the females it. This depends on what is studiedEg.

Standard Deviation Cheat Sheet Wikihow Statistics Math Standard Deviation Data Science Learning
But unusual values called outliers affect the median less than they affect the mean.

. The formula to find the variance of a dataset is. Use the mean to describe the sample with a single value that represents the center of the data. So if the standard deviation of.
Standard Deviation Standard Deviation often abbreviated as Std Dev or SD provides an indication of how far the individual responses to a question vary or deviate from the mean. Low standard deviation means data are clustered around the mean and high standard deviation indicates data are more spread out. The solution as described earlier is to divide the mean difference by the SD in each RCT.
SD tells the researcher how spread out the responses are are they concentrated around the mean or scattered far wide. Standard Deviation Standard Deviation often abbreviated as Std Dev or SD provides an indication of how far the individual responses to a question vary or deviate from the mean. The variance typically denoted as σ2 is simply the standard deviation squared.
But unusual values called outliers affect the median less than they affect the mean. In other words extreme values occur more frequently. The SMD for each RCT can now be pooled with weights assigned to each SMD as described earlier.
The median and the mean both measure central tendency. Did all of your respondents rate your. If the differences themselves were added up the positive would exactly balance the negative and so their sum would be zero.
That is the mean difference expressed in units of SD. Thus for each RCT we obtain a value that is known as the standardized mean difference SMD. The median and the mean both measure central tendency.
Use the mean to describe the sample with a single value that represents the center of the data. For each value find its distance to the mean For each value find the square of this distance Find the sum of these squared values Divide the sum by the number of values in the data set Find the square root of this What is standard error. The standard deviation SD tells you the extent to which individual values of the data differ from the mean.
Sample standard deviation. It is approximately from mean 33 SD to mean 33 SD. While the mean identifies a central value in the distribution it does not indicate how far the data points fall from the center.
Where μ is the population mean xi is the ith element from the population N is the population size and Σ is just a fancy symbol that means sum. A SD 5 would mean on an average individual values differ from the mean by 5 If the data is normally distributed about the mean then one can also gauge the range of the data. Basically a small standard deviation means that the values in a statistical data set are close to the mean or average of the data set and a large standard deviation means that the values in the data set are farther away from the mean.
To find the sample standard deviation take the following steps. With samples we use n 1 in the formula because using n would give us a biased estimate that consistently underestimates variability. Many statistical analyses use the mean as a standard measure of the center of the distribution of the data.
Many statistical analyses use the mean as a standard measure of the center of the distribution of the data. The standard deviation is a summary measure of the differences of each observation from the mean. Calculate the difference between the sample mean and each data point this tells you.
Understanding the standard deviation is crucial. Standard deviation can be difficult to interpret as a single number on its own. The higher the mean score the higher the expectation and vice versa.
For examples suppose you are measuring customer satisfaction with a new product using a 5-point Likert Scale with a range 0 not at all satisfied to 5 extremely satisfied. SD tells the researcher how spread out the responses are -- are they concentrated around the mean or scattered far wide. Calculate the mean of the sample add up all the values and divide by the number of values.
σ2 Σ xi μ2 N. Consequently the squares of the differences are added. These steps are as followsCalculate the mean of your data setSubtract that mean from each of the scores in your data set to determine the individual deviation of each score from the meanSquare each of those individual deviationsSum all of the squared deviationsDivide that sum by one less than the sample size N1.
The steps in calculating the standard deviation are as follows. Number of values in the sample. A standard deviation close to zero indicates that data points are close to the mean whereas a high or low standard deviation indicates data points are respectively above or below the mean.
The sample standard deviation formula looks like this. Higher SD values signify that more data points are further away from the mean.

Standard Deviation Approximately 68 Of All Observations From Repeated Samples Would Fall Within One Standard Devi Statistics Math Math Resources Medical Math

Pin On Helpful Guides Resources

Summary Measures Central Tendency Mean Median Mode Midrange Quartile Midhinge Summary Measures Standard Deviation Social Science Research Mean Median And Mode
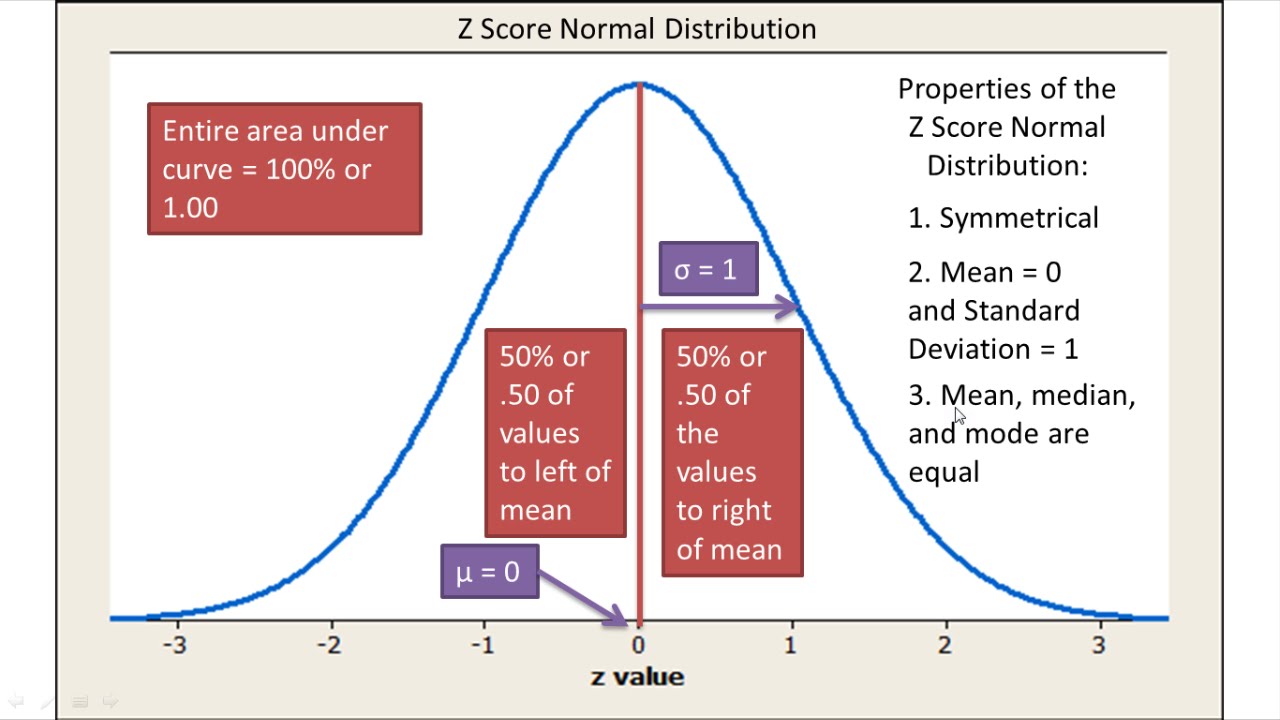
Normal Distribution And Z Scores Explained Introductory Statistics Statistics Notes Statistics Math Normal Distribution

On This Page You Ll Find A Number Of Resources For Understanding The Research Methods Used In Psychology A Research Methods Data Science Learning Ap Statistics

Variance And Standard Deviation Ccss Math Data Science Learning Mathematics Education

Stats Symbols Cheat Sheet Statistics Symbols Statistics Cheat Sheet Statistics Notes

Correlation Coefficient R Calculator

Normal Curve And Standard Deviation Z Scores Stanines Percentiles Sat Act Iq

Statistics 101 A Tour Of The Normal Distribution Normal Distribution Social Science Research Speech And Language

2 What Is Standard Deviation Coolguides Data Science Learning Statistics Math Research Methods

Measures Of Central Tendency And Variability

Ancova In Spss Understanding And Reporting The Output Spss Statistics Quantitative Research Data Analysis

How Do I Report Independent Samples T Test Data In Apa Style Data Social Work Research Sample Resume

Standard Deviation Homework Teaching Resources Standard Deviation Math Resources Math Formulas




No comments for "how to interpret mean and standard deviation in research"
Post a Comment